Carbohydrates
------------------ Work in progress -----------------
Carbohydrates are organic molecules that contain carbon, oxygen and hydrogen and are the most abundant organic compounds in nature. They serve as forms of energy source and storage and structural components for plants and some animals [Champe]. They have the basic formula (CH2O)n hence the name Carbohydrate or hydrate of carbon. Important carbohydrates in brewing are simple sugars (e.g. glucose, fructose), complex sugars (e.g. maltose, sucrose, maltotriose), dextrins and starches. But glucans, pectins and gums are also carbohydrates.
The following sections give insight into the structure of carbohydrates important in brewing. Some are more and others (e.g. lactose and sucrose) are less important in mashing but may be used at other places in the brewing process.
Contents
Monosaccharides
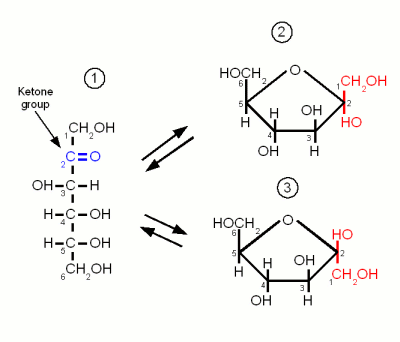
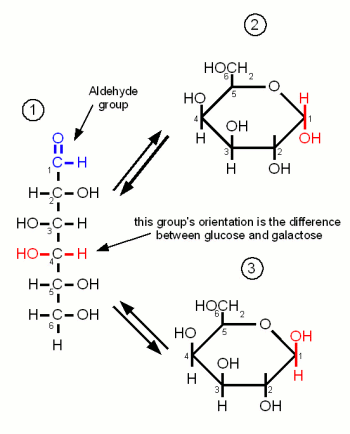
Monosaccharides are the simples carbohydrates and have the basic formula CnH2nOn. They are the building blocks of the more complex carbohydrates. The monosaccharides important to brewing, Glucose, Galactose and Fructose, are hexoses which contain 6 carbon atoms. They differ either in their carbonyl group or the orientation of the OH and H groups along the carbon chain. The carbonyl group is the group that contains the oxygen that is linked twice to a carbon atom. Either to the same carbon atom or tow different atoms from the same chain. Glucose and Galactose are adelose sugars and have an aldehyde group (Figures 1 and 3) as their carbonyl group and Fructrose is a ketose sugar and has a Ketone group (Figure 2).
Monosaccharides may exist in a open chain or in a ring configuration. But for monosaccharides with more than five carbons only less than one percent of the molecules will be in the open chain configuration. The rest is in the ring configuration. The rings are formed by the oxygen atom from the carbonyl group binding to another carbon atom of the chain.
By convetion the carbon atoms are numbered such that the highest numbered carbon is farthest away from the carbonyl (aldehyde or ketone) group.
Glucose
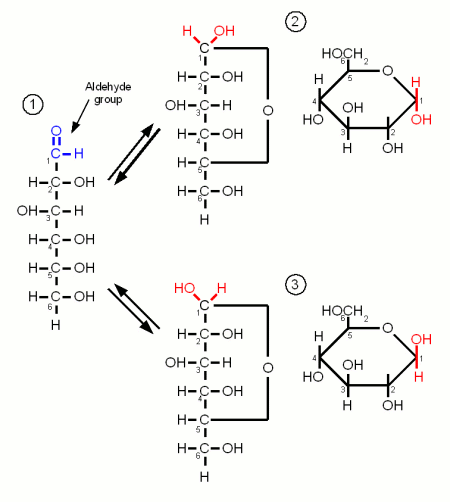
Glucose is by far the most important monosaccride in brewing. It is the building block for starch and thus produced during mashing. When the oxygen of the aldehyde group also binds to carbon atom 5 the molecule forms the ring typical for carbohydrates. The resulting molecule is called glucopyranose and depending on the orientation of the OH group on carbon 1 the molecule may be in the α or the β configuration. The difference is subtle but becomes important later when the glucose binds to other molecules to form more complex sugars. At this point α vs. β configuration becomes permanent and makes the difference between being convertible by mash and yeast enzymes or not.
But as long as the glucose molecule on its own both configurations coexist in an equilibrium and can change between the configurations by changing back to the open chain and back to the ring in the other configuration
Fructose
Like glucose, fructose is also a hexose sugar but unlike glucose it is a ketose sugar because it has a ketone group as its carbonyl group. This group contains carbon 2 (instead of the carbon 1 that is included in glucose's aldehyde group) and as a result the ring that is formed by the oxygen atom of that group binding to carbon 5 has a pentagon shape in the Hanworth projection (Figure 2).
Fructose has no importance to mashing. It is only present in malt in very small amounts. It may come into beer in substantial amounts through the addition of fruit juices, sucrose or invert sugar.
Galactose
Galactose is of no importance to mashing as it is neither present in malt nor the produced wort. It's only importance to brewing is through the addition of lactose, which is made of glucose and galactose, as a sweet by unfermentable sugar in certain beer styles (e.g. milk stouts). Like glucose it is an adelose sugar but it differs from glucose in the orientation of the OH group on carbon 4.
Disaccharides
The glycosidic bond
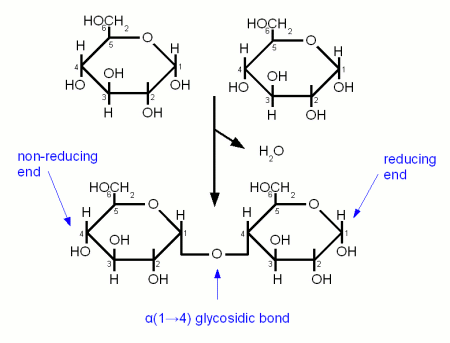
A glycosidic bond is formed when the carbonyl group of one monosaccharide reacts with a hydroxyl (OH) group of another molecule and water is eliminated [Vaclavik]. It is the "glue" that holds together monosaccharides to form more complex carbohydrates. When a glycosidic bond is formed the molecule with the carbonyl group that is involved in the bond gets locked into the α or β configuration. Enzyme can distinguish between these two types of bonds and that's why it is important to note the type of a bond. α links hold together fermentable carbohydrates (disaccharides and trisacharides) or carbohydates that can be made fermentable in mashing (dextrins and starches) while β links are the links that hold together structural malt components (cellulose, β-glucans). Another convention is to note which carbon atoms are involved in the bond. A α-1,4 (or α(1→4)) glycosidic bond is between carbon 1 (carbonyl group) of one molecule and carbon 4 of the other molecule.
reducing vs. non-reducing sugars
If a sugar has a free carbonyl (aldehyde or ketone) group, it is called a reducing sugar. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars as their carbonyl group is not involved in any bond to another molecule. Reducing sugars are able to take part in browning reactions with amino acids called Maillard reactions while non-reducing sugars aren't. But reducing and non-reducing sugars are able to caramelize.
In mashing it is important to distinguish between the reducing and the non-reducing end of a glucose chain as enzymes like beta amylase can only work on the non reducing end. The reducing end is the end with the free carbonyl group (carbon 1 for glucose) and can attach to other glucose chains through a glycosidic bond.
Sucrose for example is a non-reducing sugar as both the aldehyde group of the glucose and the ketone group of the fructose are involved in the α(1→2) link that holds both these molecules together. But sucrose can be converted to the reducing sugars glucose and fructose by making invert sugar through the use of an enzyme (intertase) or through the application of heat in an acidic environment.
Maltose and lactose are examples for disaccharides that are reducing sugars.
Maltose and Cellobiose
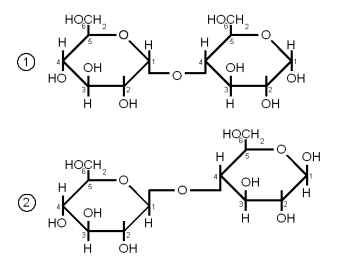
Both Maltose and Cellobiose consist of 2 glucose molecules linked. In maltose they are liked with an α(1→4) link while in Cellibiose they are linked with a β(1→4) link. The result is that maltose can be fermented by yeast while cellibose cannot.
Maltose is the most abundant sugar in wort and hence very important in brewing. It is created by the enzymatic hydrolization (degradation) of starch. Cellobiose is the building block of cellulose and has no importance in brewing as it is not degraded by mash enzymes.
Sucrose
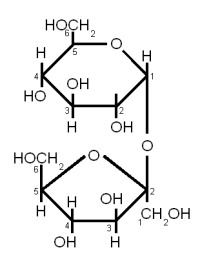
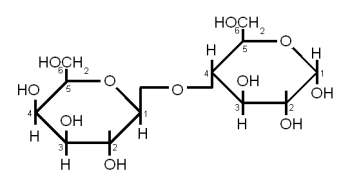
Sucrose is a disaccharide consisting of Glucose and Fructose connected together with an α(1→2) bond (Figure 6). Sucrose is also known as white or table sugar and is produced from sugar beets or sugar cane. While it is present in malt in small amounts (~ 5% of carbohydates) but is only affected little by mashing and survives into the sweet wort. More substantial amounts of Sucrose may be added as kettle adjunct or when the beer is primed with table sugar. Sucrose is a non reducing sugar.
Lactose
Lactose, also known as milk sugar, cannot be metabolized by yeast and is used used in some styles to add sweetness to the finished beer. It is neither present in malt nor a result of mashing and has to be added in the kettle.
Lactose consists of galactose and glucose connected linked together with a β(1→4) link.
Raffinose and Melibiose
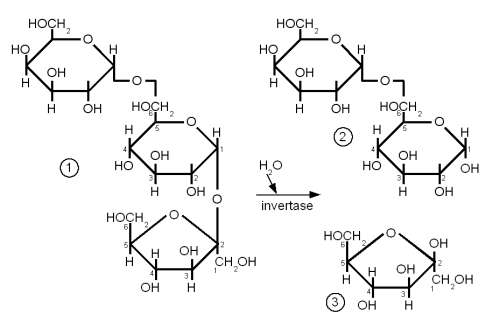
While Raffinose is not a disaccharide it should be covered here together with melibiose.
Raffinose is absent from brewing wort and melibiose is only present in very small amounts but both sugars are frequently mentioned in connection with the difference between ale yeast (s. cerevisiae) and lager yeast (s. pastorianus).
Melibiose is a disaccharide that is formed by galactose and glucose linked together with a β(1→6) glycosidic bond. Raffinose is a trisaccharide that is formed by attaching a fructose molecule to melibiose’s glucose molecule with an α(1→2) bond. Lager yeasts can completely ferment melibiose and raffinose while ale yeas can only ferment a third of raffinose and no melibiose. Both yeasts have the enzyme invertase between their cell wall and cell membrane. This enzyme breaks the splits the α(1→2) bond of raffinose and creates melibiose and fructose just as it splits the same link in sucrose to create glucose and fructose. The fructose molecule can be transferred into the cell and metabolized by both ale and lager yeasts but only lager yeasts produce the necessary enzyme (α-galactosidase) to break the melibiose into galactose and glucose which can then be metabolized. So when it is said that ale yeast can only ferment one third of raffinose it means that it can only ferment one third of each raffinose molecule and not one third of the amount of raffinose molecules.
Oligosaccraides
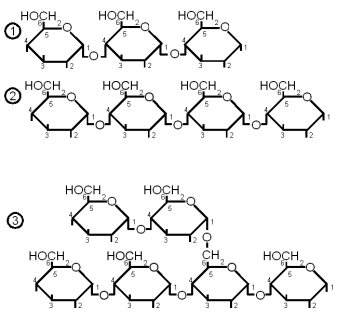
When more than 2 but less than about 10 monosaccharides are linked together the resulting sugar is called an oligosaccharide (in Greek oligos means few). In brewing only glucose based oligosaccharides are of significance. They are fragments of starch chains and depending on their length may or may not be metabolized by yeast.
- maltotriose: 3 glucose molecules linked together with an α(1→4) bond. This sugar can be fermented by both ale and lager yeast
- maltotetralose: 4 glucose molecules linked with an α(1→4) bond. This sugar cannot be fermented by ale or lager yeast
- maltopentalose: 5 glucose molecules linked with an α(1→4) bond. This sugar cannot be fermented by ale or lager yeast
- linear dextrins: 6 or more glucose molecules linked with α(1→4) bonds. Not fermentable by ale or lager yeast
- limit dextrins: small branched glucose chains. The branch point is created by an α(1→6) bond. These dextrins stem from the branch points in amylopectin and cannot be hydrolyzed by α or β-amylase. The enzyme that can break them is limit dextrinase, but that enzyme is quickly denatured above 60 C (140F). But up to that temperature only little of the starch has be gelatinized (at least in infusion mashing) which limits the enzyme's access to branch points to work on. More information about the process of starch conversion and the enzymes that are involved in it is given in ?????. This dextrin cannot be fermented by either ale or lager yeast.
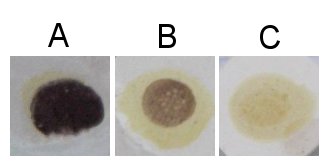
Reaction with iodine
When the glucose chains are long enough (more than about 9 glucose molecules for unbranched chains) the glucose chain (i.e. dextrine forms a helical structure that is supported by weak bonds between the hydroxyl (OH) groups of the glucose molecules. This structure can absorb one or more triiodide (I3-) ions which stains the starch. This is the chemistry between the iodine test that us used to detect the presence of starch or large dextrines. Iodine is poorly soluble in water but it can be made soluble through the presence of potassium iodine (KI) the result is triiodide (I3-) which can react with the glucose chains in the aforementioned reaction [Elmhurst].
The resulting color depends on the length of the glucose chains. Shorter chains (starting at about 9 glucose molecules in unbranched chains and up to 60 glucose molecules in branches chains) give a red color [Narziss, 2005] and these dextrines are also called erythrodextrines [Kunze, 2007]. Amylose, which consists of very long glucose chains between occasional branch points and very large dextrines gives a dark blue color while amylopectin, which has shorter glucose chains between its branch points, gives a more reddish color in the presence of iodine.
Brewing wort should show no visible reaction with iodine, This means that no glucose chains longer than about 9 glucose molecules are present. Otherwise the beer can suffer from a starch haze that is difficult to remove. This haze is actually not caused by starch but by large dextrines which become less soluble as the alcohol content increases during fermentation [Narziss, 2005].
Starch
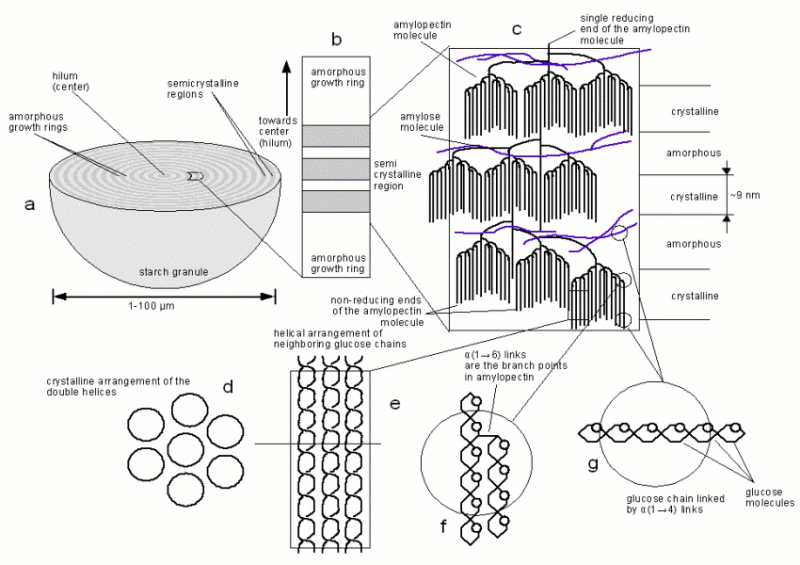
Starch is a mixture of 2 polymers of glucose: amylose and amylopectin. The glucose are linked in their α configuration, which makes them α-glucans. Through photosynthesis plants produce glucose which, as sucrose, can be transported to the roots (e.g. potato) or seeds (e.g. barley) where it is used to create amylose and amylopectin that is then stored into starch granules. While crops exist that produce amylose free starched (called waxy starches) most plant starch (including barley) consists of 20 - 26% of amylose and the rest being amylopectin.
Amylose is a polymer of glucose that contains on average 1000 glucose molecules that are held together by α(1→4) bonds. But occasional α(1→6) branch points exists which has been shown by the incomplete hydrolysis of amylose by β-amylase [Briggs, 2004]. With iodine amylose gives a characteristic black-blue color.
Amylopectin contains on average 20 times more glucose molecules than amylopectin. It is highly branched and the branch points, α(1→6) links, account for 6-7% of all bonds. The rest of the bonds are α(1→4) links. Due to the shorter length of the α(1→4) linked sections amylopectin gives a more reddish color in the presence if iodine. It's structure is shown in Figure 11. The glucose chain that contains the only reducing end, which within the starch granule is oriented towards the center or hilum of the granule is called the C chain. Attached to it with α(1→6) links are B chains. B chains can support other B chains or A chains. The A chains are the outermost chains which don't support any other chains. A and B chains forms a cluster and B chains can span and support multiple clusters. In the section, which doesn't contain α(1→6) branch points, two glucose chains will form a double helix and these double helices will then arrange in a crystalline pattern when their cross section is viewed. All these structures are held together by hydrogen bonds and will break when the thermal energy of the water is large enough. This process is called gelatinization and will be explained later.
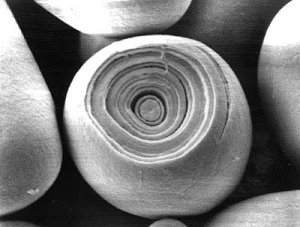
The sections where the branch points of the amylopectin are located are not crystalline, they are amorphous and may also contain amylose molecules. Yet another but larger amorphous region are the growth rings. The origin of these growth rings is not entirely clear but it has been shown that they may stem from fluctuations during the growth of the starch granule. For wheat and barley it has been shown that their starch granules will not show growth rings if the plant is grown under constant environmental conditions [Donald, 2004]
Figure 11 shows the structure of a starch granule. When a cross section is cut and viewed under an electron microscope growth rings are visible. These growth rings stem from alternating amorphous and semicrystalline regions.
In cold water starch is insoluble although some absorption of water will occur.
References
- [Valclavik] Vickie A. Valclavik, Elizabeth W. Christian, Essentials of Food Science, Third Edition, Springer
- [Champe] Pamela C, Champe, Richard A. Harvey, Denise R. Ferrier, Biochemistry, Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews
- [Elmhurst] Starch - Iodine, Elmhurst College
- [Kunze, 2007] Wolfgang Kunze, Technologie Brauer und Maelzer, 9. Auflage, VLB Berlin
- [Narziss, 2005] Prof. Dr. agr. Ludwig Narziss, Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Werner Back, Abriss der Bierbrauerei, Technische Universitaet Muenchen (Fakultaet fuer Brauwesen, Weihenstephan). WILEY-VCH Verlags GmbH Weinheim Germany, 2005
- [foodnews.ch] Saerke www.foodnews.ch
- [Donald, 2004] A. M. Donald, Understanding Starch Stucture and Functionality, Chapter 5 in Starch in Food: Structure, Function and Applications By Ann-Charlotte Eliasson, CRC Press, 2004
- types of sugar
- monosaccharides glucose, fructose, galctose
- disacchatrides maltose, succrose, lactose
- reducing/non reducing sugars
- where it is found
- glucose and 1-4/1-6 branches
- amylose
- amylopectin
- starch granule structure