This experiment accompanies Yeast Growth in Hopped Wort and it examines the effect that roasted malts have on yeast growth. I did this experiment about a month ago but haven’t found time to write about it until now. The result was that roasted malts do have an impact on yeast growth but it is unclear if that’s due to less fermentable sugars or the inhibitory effects of the melanoidens.
Setup
Just like the hopped wort experiment I prepared 500 ml purely DME based wort and 500 ml DME+carafa wort. For the latter 40 g DME and 40 g Carafa II special (ground to a powder) were boiled with water. The resulting wort was filtered and adjusted to 10 Plato extract content. An extract potenial of 75 % was assumed for the carafa. That means that the resulting wort is equivalent to wort from a grist with ~43% carafa II and ~57 % pale malt.
To create worts with increasing amounts of Carafa both worts were mixes as follows:
- 100 DME wort: no carafa
- 67% DME wort + 33% Carafa+DME wort: equivalent to about 15% Carafa in the grist
- 33% DME wort + 67% Carafa+DME wort: equivalent to about 28% Carafa in the grist
- 100 Carafa+DME wort: equivalent to about 43% Carafa in the grist
The mixed worts were inoculated with about 2 ml WY2042 yeast slurry. The counted cell density was 0.15 B/g extract. All starters were 250 ml wort in 500 ml flasks and left open while on the stir plate.
For this experiment the resulting yeast was not filtered and dried.
Results
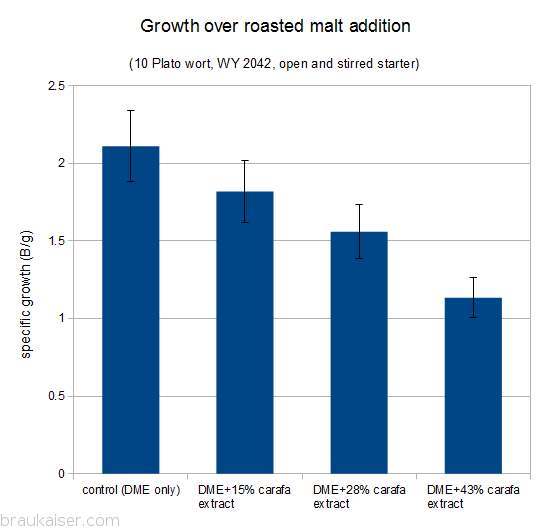
The results are shown below.
There is a clear relationship between roasted malt content and resulting yeast growth: the more roasted malt the less yeast was grown per extract.
Conclusion
At roast malt levels found in most dark beers (10 % or less) the impact on yeast growth is expected to be minimal and such worts should be suitable for yeast propagation. Extremely high levels of roasted malts should be avoided as the impact on yeast growth can be significant.
The experiment did not asses whether the reduced yeast growth was due to reduced fermentability (roasted grains provide less fermentable extract) or the inhibitory effect that melanoidens are known to have on yeast metabolism.